DC Discrete Input Modules
Discuss DC discrete input modules Like, AC discrete input modules, DC discrete input modules perform four main tasks in the PLC unit.
A review of those tasks are:
1. They sense a signal that is sent from a field device.
2. They convert input signals to the correct voltage levels for their current PLC.
3. They protect the PLC from fluctuations in a signal’s voltage or current.
4. They send sings to the processor which indicates which sensor sent the signal.
This is simply a DC voltage that is wired to the module. Same would apply for an AC input. Would simply be an AC input wired to the module. Basically, this is wired to the card.
The card must be designed to use the type, whichever type is wired to the card.
Example: a DC card needs a DC signal to the card to operate, whereas an AC card would need an AC signal to the card to operate.
Input circuits of a typical DC discrete input module
DC input modules are able to accept voltages in the amounts of 5, 12, 24, and 48. But, you must take into account the correct module for your device.
When using toggle switches and push buttons, you can simply wire the DC input to the card. DC input modules also allow the user to connect a PNP (sourcing) or NPN (sinking) transistor device to them.
Some examples of these devices are photo sensors or proximity switches.
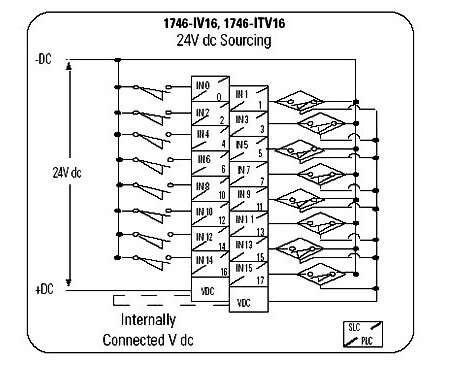
Overview of field wiring connection for a DC input module
As with the AC module, wires are connected a terminal strip. The wires are then connected from the terminal strip to the DC input card.
This allows for easier trouble shooting compared to how difficult it is to see which wire connects to which location on the card terminal strip.
Overview of a fast-responding DC input module
Fast-responding DC input modules do just what the name suggests: they are fast responding. Therefore, they should be used when speed is the most important factor.
Fast-responding DC input modules detect very short input pulses. Some devices output signals that are much faster than a PLC’s scan time and, therefore, cannot be detected using regular I/O modules.
These devices operate as “pulse stretchers”, essentially expanding the pulse time for one scan so that the PLC can detect the pulse.
When the interface is triggered, the fast-responding DC input module stretches the input signal and provides it to the processor.
This procedure also provides filtering and isolation. It is important to note that filtering causes a very shot input delay.
Examples of fast-responding input devices are:
- proximity switches
- photoelectric cells
- instrumentation equipment
As with standard DC input modules, connections to fast-responding input devices must meet the sourcing or sinking requirements of the interface for proper operation.
Most often, field devices must source a certain amount of current to the fast-responding module at the rated DC voltage



Responses